345€ or 2 x 172.50€
Build one of the most exclusive and difficult skill in the self-driving car industry and Unleash the power of 3D Localization And Mapping.
This course is currently closed and will open March/April 2025. In the meantime, be sure to join the waitlist to be notified and receive goodies while you wait.
Did you ever wonder...?
Dear friend, if you've spent some time looking for a resource to understand SLAM, then this page will show you how.
Here's the story:
Back in 2018, as I was working on Computer Vision for autonomous shuttles, I set a really ambitious challenge for myself: to learn about SLAM!
It was really exciting, and I was excited, but there was a big difficulty I didn't estimate...
I mean, have you ever tried to learn about SLAM? To code some SLAM projects? To build intuition on how the maps are created? To put algorithms inside boxes? To get a clear picture of the different approaches?
It's really hard...
I mean, just google "learn SLAM" or search on Reddit, and you'll see that the best advice looks like this:


Which contains 33 lectures and PDFs of HOURS at MIT level...
And this:
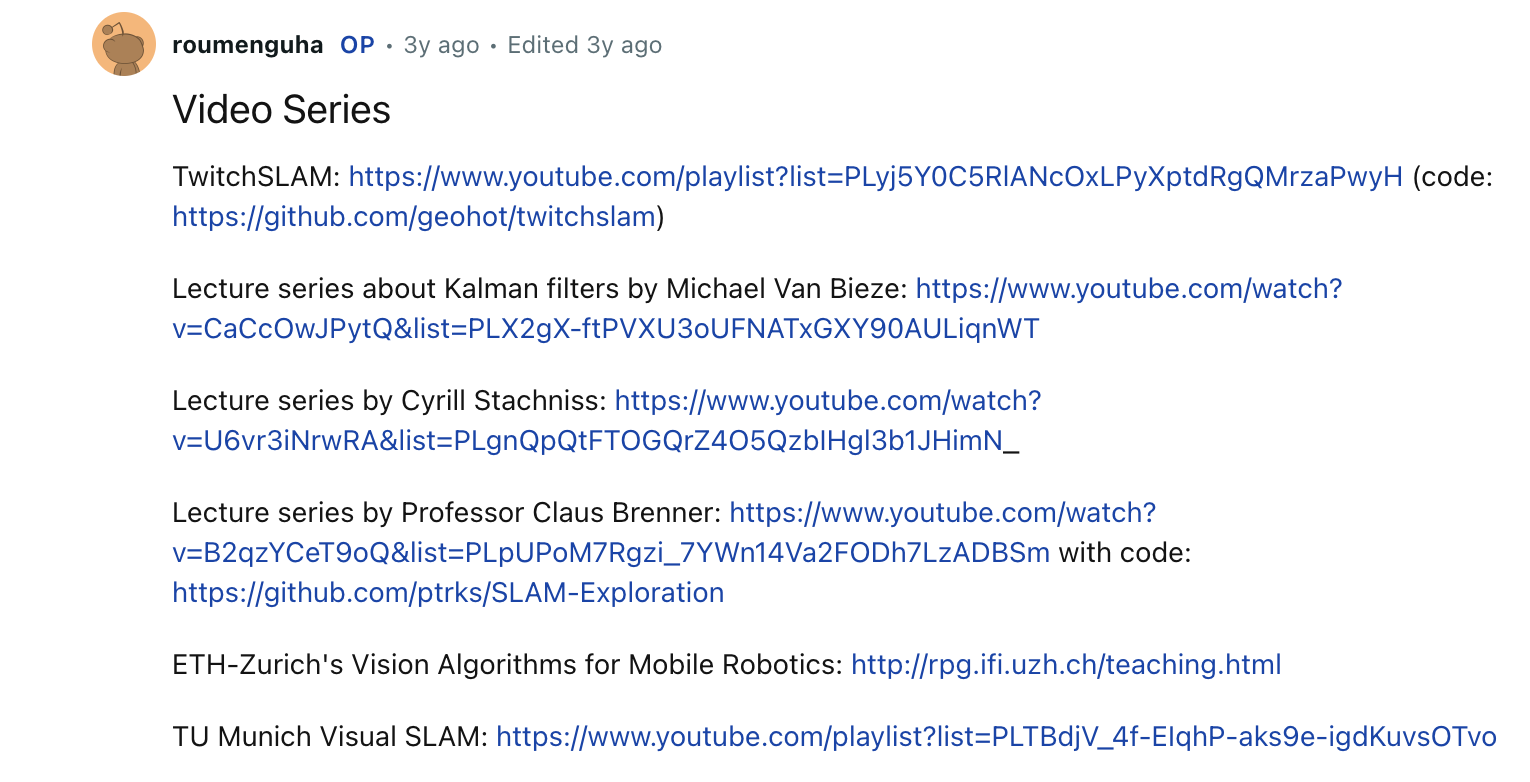
Which references YouTube playlists teaching SLAM. Go to the first video of the first one, it's over 10 hours long. And you think the others are lighter? Yeah, maybe, but you'd still need to invest 50+ hours, passively watching video lectures on YouTube and trying to "understand" atrocious maths.
Sure, there are "textbooks", like these ones:

But when you open them, they look like this:
Just what you need right? A 400+ page PDF full of maths and code, and a 40+ hour YouTube series showing you the same maths and code.
Isn't it ideal?
I mean, to be fair, these resources truly are great. Many are well written, and some teachers are really experts are what they're teaching, far more than I could ever be.
BUT
This type of content is not for everybody...
What about nice images and pictures? What about a story with a dinosaur trying to map a world? What about something oriented to beginners?
I saw two problems with these courses:
You get out of it still wondering what is SLAM, and still thinking "compared to a REAL SLAM Engineer or researchers, I merely scratched the surface"
The projects are really bad.
I mean, if you are to work on autonomous vehicles, you'll need to code real projects, not THIS:
Is the teaching giving a good understanding of SLAM? or do you get out of it feeling like you've only scratched the surface? Are the projects really relevant for a self-driving car engineer?
If you are to be a Self-Driving Car Engineer, or a 3D Computer Vision Engineer, or a SLAM Engineer, you're gonna need to build a portfolio project yourself (not just cloning a repo and running it), and you're gonna need to fully understand your topic...
And this is where it's starting to get difficult, because the alternative is to clone a state of the art SLAM algorithm, run it, and... not understanding a clue of what's happening...
And this is, I think a big problem, because it means that there is no easy and short solution to learn SLAM.
You're either going through the endless video lectures, watching people talking over maths and maths and maths for hours... Or you're going to the super simple Python script with a plot, and that doesn't make you a SLAM Engineer.
The overview: Are you able to do some kind of mindmap of the SLAM algorithms? For most engineers, the answer is no...
The lessons: Is there a simple lesson explaining topics like Graph SLAM? Or topics like Odometry? Not really...
The projects: Could you load a self-driving car "bag" and then start coding odometry? Then code your own mapping and optimization system? It's difficult to find a place for this...
And I created "THE GRAND SLAM" which was my first time teaching SLAM. But after 3+ years of feedback, I understood some of the gaps I needed to fill, such as the projects, or the overview, to come up with...
And I know that this claim is bold, and my goal is NOT to be an alternative to the 30h+ video lectures on YouTube...
-> It's to teach SLAM for Engineers rather than for researchers. This means fewer maths and more code. And if after the course, you're able to code a SLAM system and want to spend the 50 hours doing the maths, then be my guest. It will only enhance your knowledge, but this shouldn't be the only alternative you got...
Introducing...
Let me share with you some of the things you'll learn in this course, divided in 3 key modules:
Odometry: The task of estimating how much you've moved over time
Mapping: The task of building maps
Optimization: The task of building a final, global map.
MODULE 1
The first module focuses on Odometry, which is the (highly used) science of estimating where you are based on your motion.
What you'll learn:
4 Sensor Based Techniques to measure odometry (we'll see things such as odometers, IMUs, quaternions, GPS, and fusing it all using Extended Kalman Filters, ...)
A look at LOAM, a cutting-edge LiDAR Odometry And Mapping algorithm, and the difference between direct and indirect odometry in SLAM
Everything an IMU returns, and how to combine it with odometry algorithms (when studying SLAM, you'll notice that there are entire categories of algorithms using the IMU)
How to use Sensor Fusion and an Extended Kalman Filter for Robot Localization (using GPS, IMU, and other things)
An introduction to Quaternion coordinates, and why it's so used in Robotics (warning: if all you know is XYZ coordinates, you'll be surprised!)
How to use Feature Tracking & 3D Reconstruction principles to estimate the motion of a robot from a camera
How Visual Odometry Works (most of the concepts are very similar to 3D reconstruction, we'll talk about feature tracking, triangulation, pose recovery, and more ...)
The old and new secrets of LiDAR Odometry and Point Cloud Registration (you probably heard o ICP algorithms, or NDT, it's all in there!)
LiDAR Odometry Project 🎸: Implement a LiDAR Odometry pipeline using Point Cloud Registration and hardcore maths to localize a robot in the environment
If we pause a second, this project is the first you'll have to implement, and it will feature REAL self-driving car data, with a REAL pipeline. By this, I mean we won't do basic simulations on Gazebo, and we will use real-world constraints given by our data.
A look at the project:

Notice something, this is YOU coding it. We are not using a GitHub repo, we are not using pre-existing ROS functions. In this course, I want you to be in control of what's happening. This isn't a course where you'll run an algorithm and think you got it, you WILL be forced to understand the algorithms to make it work.
With this, you can notice two curves: a red representing KISS-ICP (which admitedly is a clone & run project), and a blue representing your "from scratch" implementation.
Now this is only module 1. We could have stopped here and make it an Odometry course, but I really wanted it to be a SLAM course, so here is Module 2 on Mapping...
January 2026
We just added a new Visual Odometry module teaching you the fundamentals of feature tracking, odometry estimation, pose recovery, 3D Reconstruction, and more... It contains 2 projects, where you'll learn to build and run SLAM algorithms!
MODULE 2
In Module 2, we'll build maps from visual features (Visual SLAM) and from point clouds (LiDAR SLAM). This module will be intense, but the number of skills you'll get out of it will significantly change your robotics engineer status. Let's see...
What you'll learn:
How to project 2D features in the 3D space, and the secrets of local Bundle Adjustment & 3D Reconstruction
The 5 Types of Maps used in self-driving cars, and which ones the algorithms in SLAM can build (SLAM cannot build everything, and you'll see that in some cases, it's preferable to use other types of algorithms)
An in-depth look at Filter-Based SLAM algorithms, from Extended Kalman Filters, to advanced Rao-Blackwellized particle filters, and how to implement them in ROS
A deep dive into LSD-SLAM, a dense mapping algorithm; and the difference between sparse and dense mappers
How to create 3D Maps from point cloud features, and an exploration into Lidar Odometry And Mapping using features
The "Sebastian Thrun" Graph SLAM approach, and why new algorithms are moving away from it
A detailed analysis of the Graph SLAM optimization metrics, and the core principles behind minimization algorithms
The secrets of Gauss-Newton and Levenberg-Marquardt optimization, and a special access to an MIT professor who agreed to teach the maths as part of the course
Let's pause for a second:
I assume at this point, it can feel like we'll see a lot of theory. And we will try to understand how it works. But I have to tell you exactly how much so you understand what you're going into. I believe engineers do not "need" to spend 20+ hours watching someone explaining maths equations and the non-linear least square optimization. So, I won't do this "from scratch" as part of the course. BUT, I'm giving you the option to do it if you want to via other professors whose specialty it is.
In this course, I want to explain just enough maths so you can build the projects and feel familiar with them. You should be able to code Graph SLAM matrices, you should be familiar with feature angles, quaternions and Euler coordinates, and this is part of the course.
So now let's see the practical part:
Graph SLAM Project : Code a Graph-SLAM system using Visual Fusion (LiDAR & Camera fusion) to build Sparse 3D Maps from camera features.
The project is visible up there, and you can see there's some sensor fusion involved, as well as advanced optimization algorithms.
But it's not all this course has to offer, so let's see the final module...
MODULE 3
In this final module, we'll look at the secrets behind Loop Closure, even implement a loop closure algorithm, and work with Graph optimization frameworks.
Skills you'll build:
An advanced and in-depth look at RTAB-MAP, ORB-SLAM, LSD-SLAM, and other cutting-edge SLAM systems and how they work
How to tell the difference between Visual SLAM algorithms, and the 3 key things to look for in a Visual SLAM mapper (I'll also give you some Ctrl-F words to look for in research papers to automatically understand what the algorithms you're seeing online are doing)
What is Loop Closure and how to implement it in a SLAM system
The secrets of Bag-Of-Words, and why they're still one of the most important element in SLAM
An introduction to the G2O Framework and how to optimize graphs using Non-Linear Least Square algorithms
RTAB-MAP Mini-Project 🎸: Run and parameterize a Visual SLAM system to achieve loop closure
Loop Closure Project 🎸: Engineer and Code a Visual Loop Closure algorithm to detect if a scene has previously been seen
On paper examples of 1D and 2D SLAM algorithms and how to use Information Filters to solve SLAM equations
Map Optimization Project 🎸: Learn to use the G2O framework to optimize large maps offline and refine complete mapping systems.
The ONLY REAL Mindmap of SLAM, giving you the INSTANT POWER to classify ANY SLAM ALGORITHM into a specific box (this part has been the hardest to build; no matter the 15+ surveys I read on SLAM, NONE could simplify the problem to the point where you can just put algorithms inside "boxes"; this mindmap is the ONLY one doing it)
As you can see, this last point is particularly important:
If you're reading a "Survey" today about SLAM, chances are you'll only understand part of the SLAM world. I have read 15+ different surveys, and in the end, I still wasn't sure how to "classify" SLAM algorithms. Some of them were even wrong, confusing LiDAR algorithms with Vision algorithms, and doing classification mistakes.
So I built a Complete Mindmap of the SLAM world, and included it in the course.
But it's not ALL, because to help you understand it even more, and to enhance my Mindmap, I also included:
My Notes from everybody else's SLAM surveys (other classifications you may find, other names, how to spot errors, etc...)
(About SLAM v1)
The course showed me all the way to perform a solid simulation and to play with it until I really got a good feeling how SLAM works. The course certainly is not long enough to answer all my theoretical questions but it gave me the links to investigate deeper on my own.
In the end I was able to implement SLAM on my own robot with ROS. And together with the ROS course I not only got it working but started to understand what is behind it.
Ivo Germann, Development engineer R&D, Project leader bei Zumbach AG
This course is, like my other courses, aiming to teach people who have a prior background. If you can't code, doesn't know what a Kalman Filter is, and have never been exposed to the idea of "stereo vision", things may feel too complex.
SLAM is tied to many other topics, such as:
Kalman Filters
Stereo Vision & 3D Computer Vision
Feature Tracking & Optical Flow
Point Clouds Processing
and more...
So the more you already know about these topics, the 'easier' this course will feel for you.
If you don't know any of them? The course is designed to be "friendly" anyway, by doing recaps of these topics when needed, but I would recommend to at least be familiar with these topics before joining (and you can do so via my other courses).
Yes, here is a quick list:
Maths — Matrix Multiplications, Linear Algrebra, Calculus, and Probabilities
Maths II — (if you want to understand the maths of SLAM) Complex Numbers, Quadratic Expressions, Singular Value Decomposition, Non Linear Least Squares, Quaternions & Euler Coordinates, ...
Python — All the course is in Python
Linux & ROS — The projects of this course will happen on ROS 2 to process real self-driving car recordings. It's a big plus if you understand ROS, but I made sure that not knowing it isn't blocking for you.
Both, and if you want to, you will be able to "specialize" in one of the two. Essentially, LiDAR SLAM involves SLAM + a good understanding of point clouds, and Visual SLAM involves SLAM + a good understanding of Computer Vision (stereo vision, 3D Reconstruction, Optical Flow, ...)
This course is trying to keep SLAM clear and concise, while having you coding cutting-edge projects and building a strong understanding of SLAM.
It should last around 7-10 hours to complete the course and projects, and from there, you should be good enough to get an entry level position as a SLAM Engineer. This means that after the course, you'll have several portfolios showing your skills, you'll be able to explain them, and you'll have built cutting-edge and rare skills.
But unlike some of my other courses like HydraNets, this course will NOT prepare your for a "researcher" position. In SLAM, a researcher position is achieved through MONTHS of going through the SLAM books and maths (which we won't do).
However, going to THIS SLAM course first will have you win MONTHS in your SLAM journey (even as a researcher), because at every video you'll watch, at every PDF you'll read, you'll know where this fits, why you're learning it, if it's important, and more...
Not for?
I can't think of anyon— oh, yes, it's probably not for you if:
🔴 You don't validate the prerequisites and don't feel excited by the content shown above (obvious, but worth mentioning)
🔴 You're judging a course by its duration, and expect 300+ hours of maths — sorry, in this case, go to YouTube. If anything, I'm trying to help you finish as fast as possible, this month if you can, let's not lose you in endless amount of content.
🔴 You just want to know how to run a SLAM algorithm with ROS without really opening the black box.
🔴 Or on the other side, you want to understand every single SLAM algorithm, math formula, and code block. We'll open the black box, but we'll stick to a good understanding, not research-level work.
🔴 You don't want to work on 3D Computer Vision, SLAM, or real robots.
On the other hand, here is who this course is for:
🟢 You've tried to learn SLAM in the past but found it difficult, hard to vulgarize and reexplain, and still feel like a beginner
🟢 You have some good prerequisites, and feel ready to experience the SLAM'ANIA
🟢 You've always wanted a way to code a SLAM algorithm yourself, but always felt like it was either too beginner or too advanced.
🟢 You are ambitious, resilient, and want to stand out in the market by building one of the most hard-to-find skill to companies.
This course is the ONLY SLAM course that has a focus on IMPLEMENTATION of SLAM algorithms.
While other courses are cloning repos and running ROS commands, or using super-simple "plot" projects, this one really opens the black box and "unleashes" your ability to code SLAM algorithms.
This is important, because this is how you're actually confident in your understand of SLAM, and can work on things such as 3D Reconstruction, Odometry, or Visual Inertial Odometry, or Map Optimization and more...
345€ or 2 * 172,50€
Build one of the most exclusive and difficult skill in the self-driving car industry and Unleash the power of 3D Localization And Mapping.
This course is currently closed and will open March/April 2025. In the meantime, be sure to join the waitlist to be notified and receive goodies while you wait.